Comprehensive PFAS Management Strategies for Water Sources
Comprehensive PFAS Management Strategies for Water Sources
Blog Article
Advanced Techniques for Reliable PFAS Contamination Removal
The consistent challenge of PFAS contamination demands the exploration of innovative removal techniques that can successfully address these damaging compounds. Cutting-edge modern technologies, such as sophisticated oxidation processes and different adsorption techniques, have emerged as encouraging solutions in mitigating PFAS from affected atmospheres.
Comprehending PFAS Residences
Although per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) have actually been extensively utilized in various commercial and consumer products as a result of their one-of-a-kind properties, their persistence in the setting positions considerable difficulties to public health and safety. PFAS are a team of synthetic chemicals identified by a carbon-fluorine bond, one of the best chemical bonds understood, which contributes to their outstanding security and resistance to destruction. This security enables PFAS to accumulate in the setting and living organisms, leading to potential negative health and wellness effects.
The hydrophobic and oleophobic nature of PFAS makes them especially reliable in applications such as non-stick finishings, stain-resistant textiles, and firefighting foams. These same residential or commercial properties add to their ecological persistence, as PFAS do not quickly break down with all-natural processes. In addition, their widespread usage has actually resulted in common contamination of water resources and dirts, making complex removal efforts. Recognizing the chemical residential properties of PFAS is crucial for creating reliable techniques to take care of and alleviate their environmental effect. The distinct qualities of these substances necessitate a nuanced strategy to attend to the challenges posed by their presence in ecological communities and potential human direct exposure.
Innovative Remediation Technologies
The persistence of PFAS in the atmosphere has stimulated the development of cutting-edge removal innovations targeted at successfully removing these contaminants from impacted environments. Among one of the most promising techniques are sophisticated oxidation processes (AOPs), which utilize powerful oxidants to damage down PFAS compounds right into less damaging compounds. AOPs can be customized to target specific PFAS frameworks, improving their efficiency.
An additional emerging modern technology is making use of adsorption media, such as triggered carbon and ion exchange resins, which can uniquely record PFAS from contaminated water. These materials have shown substantial removal performances, although regular replacement and regrowth are essential to preserve performance.
Membrane layer purification methods, consisting of reverse osmosis and nanofiltration, are likewise acquiring traction in PFAS remediation. These techniques can efficiently separate PFAS from water, supplying a feasible option for dealing with infected sources. Furthermore, thermal therapy techniques, such as incineration, can decompose PFAS into safe byproducts, though they call for cautious monitoring to manage emissions.
Collectively, these innovative remediation technologies stand for substantial developments in the recurring battle against PFAS contamination, supplying various methods to restore affected environments and secure public health and wellness.
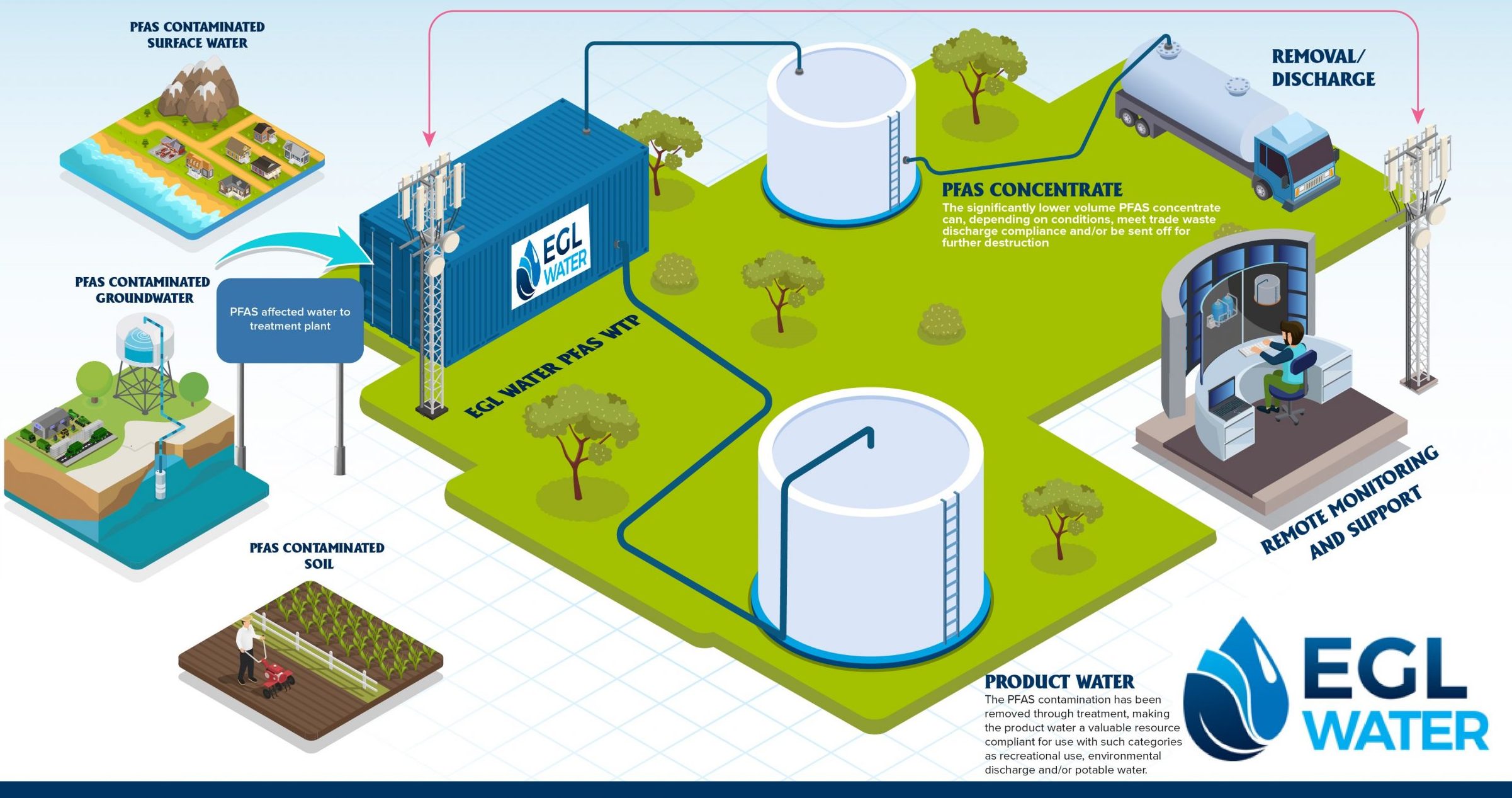
Bioremediation Methods
Bioremediation methods supply an appealing strategy to resolving PFAS contamination by harnessing the natural abilities of microbes to deteriorate these persistent substances (m270 waste management). This approach entails making use of germs, fungis, and other microbes that can metabolize or change PFAS materials right into much less harmful results
Current improvements in molecular biology and environmental microbiology have improved our understanding of microbial neighborhoods and their potential functions in PFAS destruction. Researchers are actively exploring details stress of microorganisms, such as Pseudomonas and Bacillus, which have actually shown the capacity to break down certain PFAS compounds.
In situ bioremediation methods, where bacteria are boosted directly in infected environments, can be especially effective. This approach frequently involves the application of nutrients or electron donors to advertise microbial growth and task. Additionally, ex lover situ methods, such as bioreactors, enable for regulated problems that can enhance destruction rates.
Regardless of the assurance of bioremediation, challenges continue to be, including the complex nature of PFAS compounds and the need for considerable area screening - m270 waste management. Continued research and advancement will certainly be important to fine-tune these strategies and examine their effectiveness their website in diverse ecological contexts
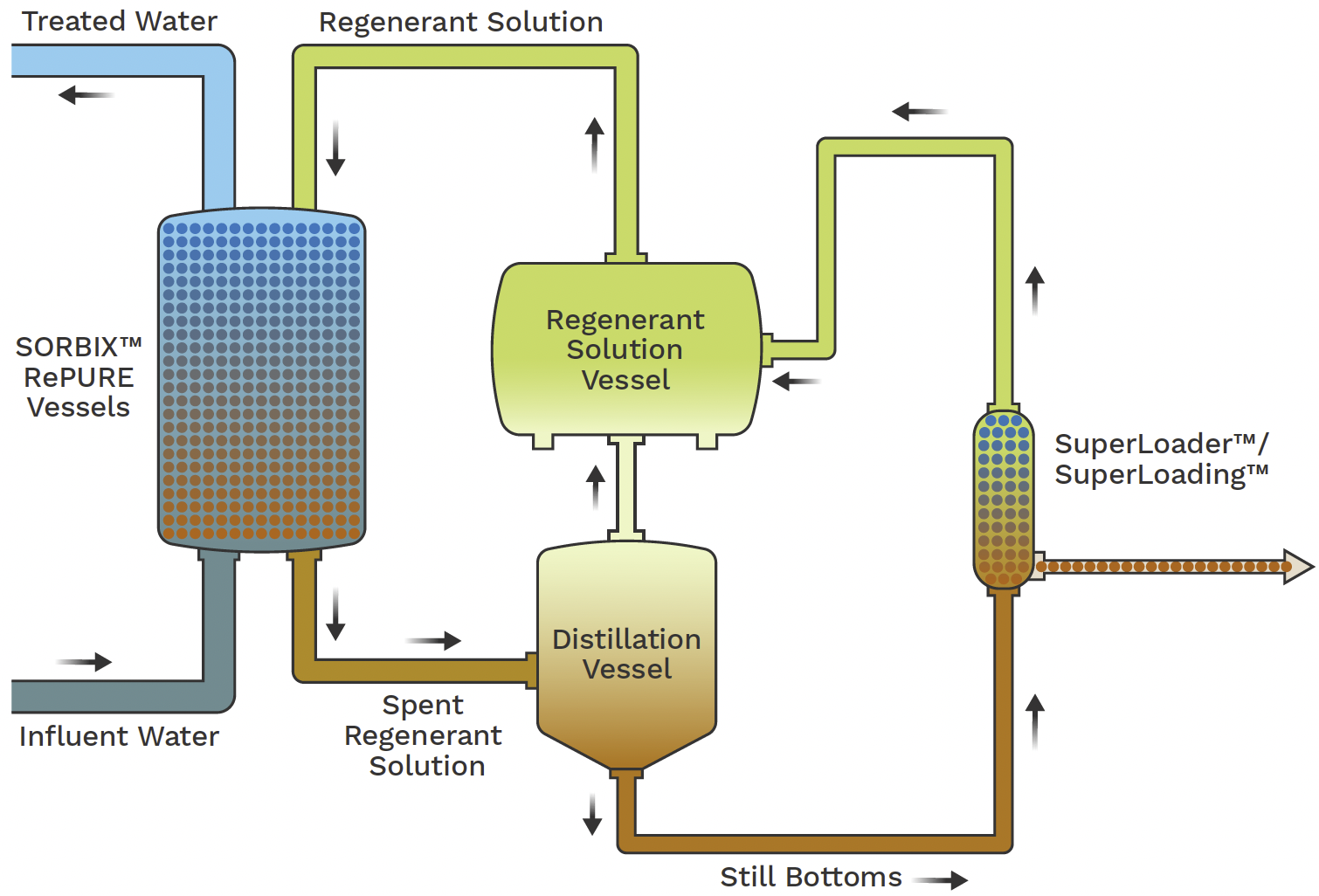
Adsorption and Filtering Methods
Attending to PFAS contamination commonly includes utilizing adsorption and filtration techniques, which are designed to get rid of these consistent chemicals from water and soil. Amongst the numerous strategies, turned on carbon adsorption is extensively made use of due to its high surface and porosity, making it possible for efficient trapping of PFAS molecules. Granular triggered carbon (GAC) systems are especially preferred for treating big quantities of contaminated water, while powdered triggered carbon (SPECIAL-INTEREST GROUP) can be made use of for smaller-scale applications.
Ion exchange materials likewise reveal pledge in PFAS elimination, functioning by trading PFAS ions with less dangerous ions in the water. This technique has demonstrated effectiveness in concentrating PFAS substances, facilitating their succeeding removal. Furthermore, membrane layer filtration strategies, such as reverse osmosis and nanofiltration, run by using semi-permeable membrane layers to different PFAS from water, efficiently minimizing their focus.
While these approaches are effective, they need to be meticulously chosen based on the particular PFAS substances existing and the environmental context. Continuous improvements This Site in products scientific research and engineering are resulting in the development of unique adsorbents and filtration systems that improve removal efficiencies and lower operational expenses, therefore enhancing total removal initiatives.
Regulatory and Policy Factors To Consider
Just how can effective regulative structures enhance the monitoring of PFAS contamination? Detailed policies are vital to guarantee a coordinated and robust reaction to the difficulties postured by per- and polyfluoroalkyl materials (PFAS) Regulations can develop clear guidelines for tracking, reporting, and remediating PFAS-contaminated sites, fostering responsibility among sectors and public entities. (m270 waste management)
Furthermore, economic incentives and grants can be integrated right into plans to urge the adoption of innovative remediation technologies. Policymakers ought to likewise prioritize r & d, making sure that emerging techniques for PFAS elimination are validated and carried out properly.
Moreover, public understanding and engagement are vital elements of any kind of governing strategy, equipping areas to advocate for their wellness and security. Inevitably, a well-structured regulatory environment will not just improve the monitoring of PFAS contamination however also advertise sustainable techniques that safeguard future generations.
Verdict
In recap, the intricacy of PFAS contamination demands the fostering of advanced remediation approaches. Cutting-edge modern technologies such as advanced oxidation processes, adsorption strategies, and membrane filtering have check over here actually shown significant efficiency in getting rid of these persistent compounds from polluted water resources. Furthermore, regulative frameworks need to evolve to sustain the application of these innovations, making sure safe and reliable monitoring of PFAS pollutants. Proceeded research and development in this area continue to be critical to attending to the difficulties posed by PFAS contamination.
Report this page